Pulsed Field Ablation for Treating Atrial Fibrillation
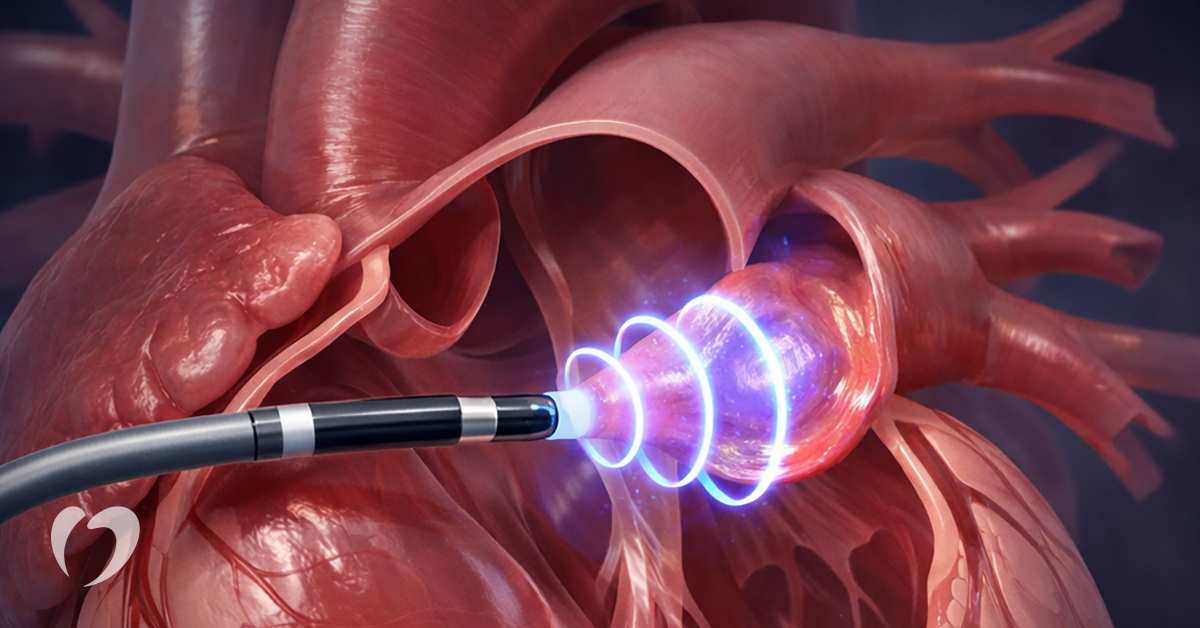
Pulsed field ablation (PFA) is an emerging catheter-based treatment for atrial fibrillation (AFib) that targets the heart’s abnormal electrical signals using controlled electrical pulses.
For patients with AFib, catheter ablation is a common treatment option when symptoms are not well controlled with medication. Traditionally, catheter ablation procedures have used heat or cold energy to target areas of heart tissue responsible for irregular electrical signals.
What is pulsed field ablation?
Pulsed field ablation is an innovative, nonthermal ablation technique that uses short, controlled electrical pulses to disrupt abnormal electrical pathways in the heart. These pulses affect heart muscle cells in a way that interrupts the electrical signals causing AFib.
Because pulsed field ablation doesn’t use heat, it’s less likely to affect surrounding tissue compared to other types of ablation. Its ability to more specifically target heart tissue only is one of the reasons PFA has generated interest as a treatment option for atrial fibrillation.
How pulsed field ablation differs from traditional ablation
Most ablation procedures for AFib focus on isolating the pulmonary veins in the heart, which are a common source of irregular electrical activity. The primary difference between ablation approaches is the type of energy used.
Radiofrequency ablation uses heat delivered through a catheter (a thin tube) to treat specific areas of heart tissue. After the procedure, small areas of scar tissue form that block the incorrect electric signal in the heart. It has been used for many years and is a well-established treatment option.
Cryoablation treats heart rhythm problems by using cold energy to carefully target small areas of heart tissue. It’s a long-standing, widely used procedure that has helped many patients restore a normal heart rhythm.
Pulsed field ablation uses short electrical pulses to treat the targeted heart tissue while reducing exposure to nearby structures, including the esophagus and nerves. Like all ablation procedures, PFA carries some risks, including bleeding, vascular complications, pericardial effusion (excess fluid in the sac surrounding the heart), or stroke. Outcomes depend on individual patient factors.
Who may be a candidate for pulsed field ablation?
Ablation is typically considered for patients with AFib who continue to have symptoms despite medication, cannot tolerate medications, or prefer a rhythm-control approach. Whether pulsed field ablation is appropriate depends on several factors, including the type of AFib, prior treatments, heart anatomy, and overall health.
Pulsed field ablation may be an option for some patients with:
- Symptomatic AFib that persists despite medication
- No contraindications to catheter-based procedures
Not every patient is a candidate for pulsed field ablation. An electrophysiologist will evaluate each patient individually to determine the most appropriate treatment option.
How does recovery compare to traditional ablation?
From a patient perspective, recovery after pulsed field ablation is similar to recovery after other catheter ablation procedures. The procedure is performed using catheters inserted through blood vessels, and most patients go home the same day or after a short hospital stay.
After ablation, patients are typically advised to:
- Limit strenuous activity for a short period
- Monitor the catheter insertion site for swelling or bleeding
- Watch for symptoms like chest discomfort, shortness of breath, or changes in heart rhythm
- Continue prescribed medications, including blood thinners, as directed
Fatigue and temporary rhythm changes can occur during the healing process, regardless of the ablation method used. Your care team will provide specific guidance based on your procedure and health history.
Considering pulsed field ablation
Pulsed field ablation is one of several treatment options available for managing atrial fibrillation. Advances in ablation technology continue to expand the tools available to electrophysiologists, which allows care teams to better tailor treatment to each patient’s needs.
If you are experiencing symptoms, such as palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath, or reduced exercise tolerance, an evaluation with an electrophysiologist can help determine whether an ablation may be appropriate.
If you have questions about your heart rhythm or would like to explore whether a pulsed field ablation may be appropriate for you, our team at the OHH Heart Rhythm Institute is here to help you understand your options. Contact us today to schedule your appointment.
